What are Keywords?
Are you looking to get more people to visit your website? Wondering what makes them click? You might have heard about SEO and ads, but the real game-changer here is keywords. Keep reading to find out how to pick the right target keywords to increase your site traffic and make search engines work in your favor—all without breaking the bank.
Now, let's figure out how you can higher up in search results and source qualified leads!
First of all, what is a keyword?
So, what exactly are keywords? The meaning of keywords is essentially the words or phrases people type into search engines when looking for something. If you're searching for "buy leather bags online" or "best burger bar in Chicago," those are your keywords. They can be as short as one word, like "dating," or as long as a phrase, such as "dating site UK." The key is to find out what terms people are using to search for services or products like yours. Then, incorporate those keywords into your website's content. Doing this helps search engines find you, bringing more people to your site. For those looking to enhance their SEO strategies further, expert SEO help can provide tailored solutions to ensure your website ranks higher and attracts the right audience.
Who needs keywords? Everyone who owns a website!
Whether you have a small online shop or a large enterprise, keywords are essential. This is especially true if you're using paid ads on search engines. Even niche websites with fewer visitors need well-chosen keywords. Search engines scan your content to identify these terms, which helps them categorize your site, determine its rank in search results, and decide which ads to display. In essence, your choice of keywords has a significant impact on your online visibility.
How to choose the right keywords?
You might think that using broad keywords will attract more visitors to your site. But hold on a second! The downside is that many other websites are likely using the same broad terms or SEO phrases. This can make your site harder to find and might attract visitors who aren't actually interested in what you're offering.
Google offers helpful tools for keyword research, but it can also be useful to jot down a list starting with general terms and gradually getting more specific. Think like a searcher: What words or phrases would you use to find what you're offering? This exercise can help you pinpoint effective keywords that align with what people are actually looking for.
Don't guess; discover keywords easily!
There are plenty of great tools that can show you the target keywords people use to find services like yours.
• Keyword Planner Tool by Google
What is Google Keyword Planner?
Google Keyword Planner is a useful tool for keyword research. Developed by Google, it scans the internet to recommend keywords that fit your needs, both general and specific. The tool also shows you how often each SEO keywords are searched, along with additional SEO keyword examples and ideas. Plus, it offers information on cost-per-click and potential price changes, helping you budget effectively. Because it streamlines much of the research process, it's worth checking out whether you're a digital marketer or a small business owner.
Best keywords for your business!
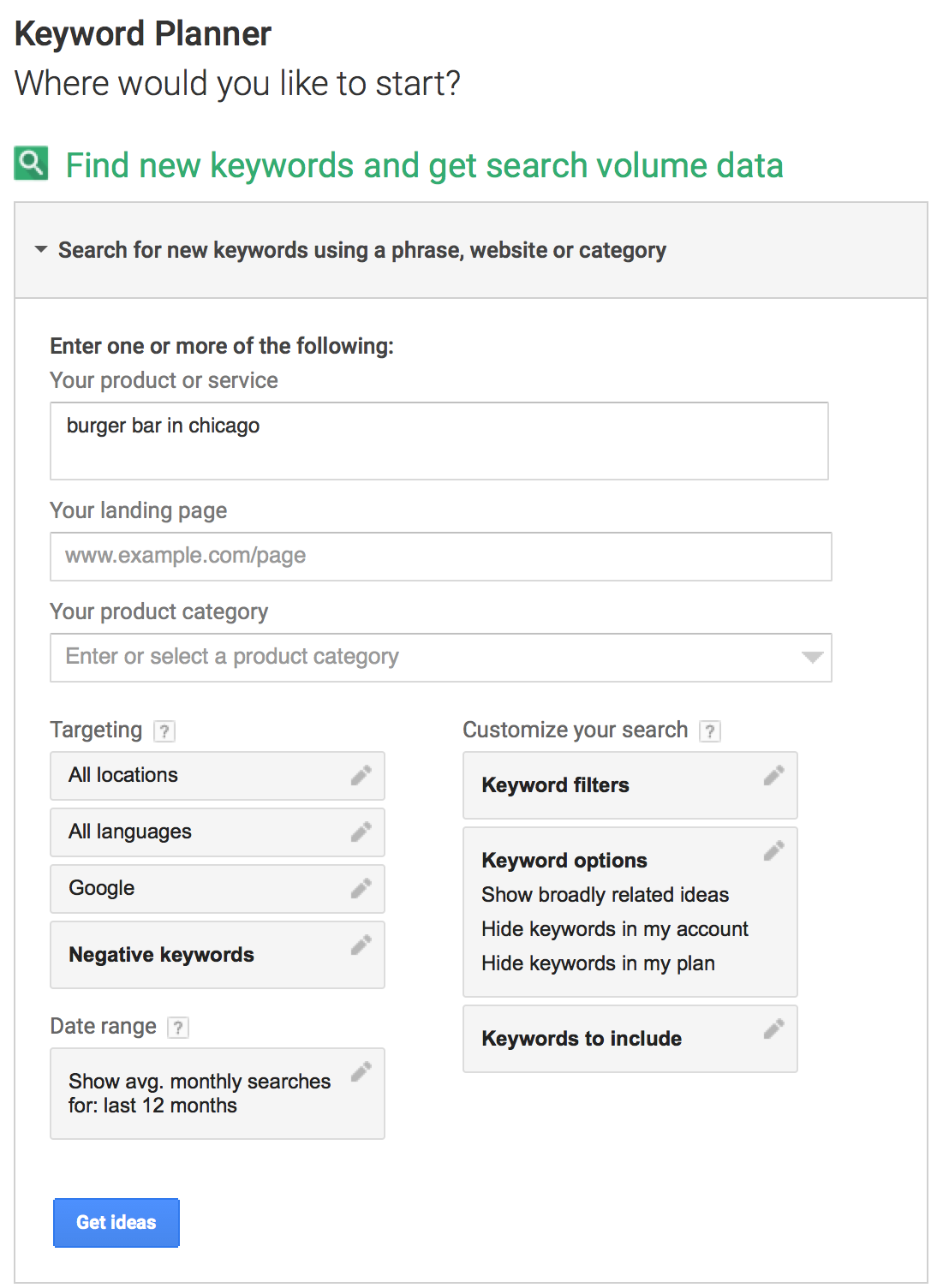
Imagine you own a burger bar in Chicago and have a website featuring your menu and location. Your goal is for people to find you on Google and come dine at your restaurant.
*It's essential to include "Chicago" in your keywords to attract local searchers.
I have added "burger bar in Chicago" to the Keyword Planner Tool, which we can suppose is the most relevant keyword to my business.
Now, let's analyze the results provided by Google.
The initial keyword we picked didn't hit the mark, showing a low monthly search volume of just 10-100. But not to worry, Google Keyword Planner suggests better options.
Now, let's analyze the results provided by Google.
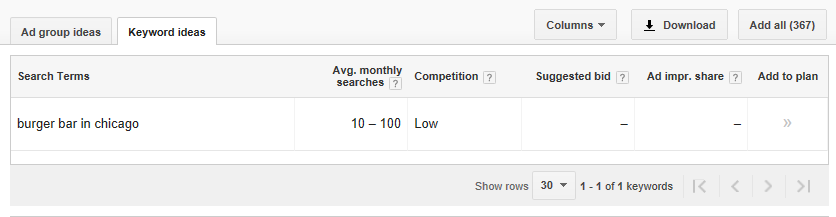
According to the results, we didn’t choose the best keyword, as it has a very low monthly search volume (10 - 100), but Google Keyword Planner is smart enough to suggest keywords similar to the one I have added initially.
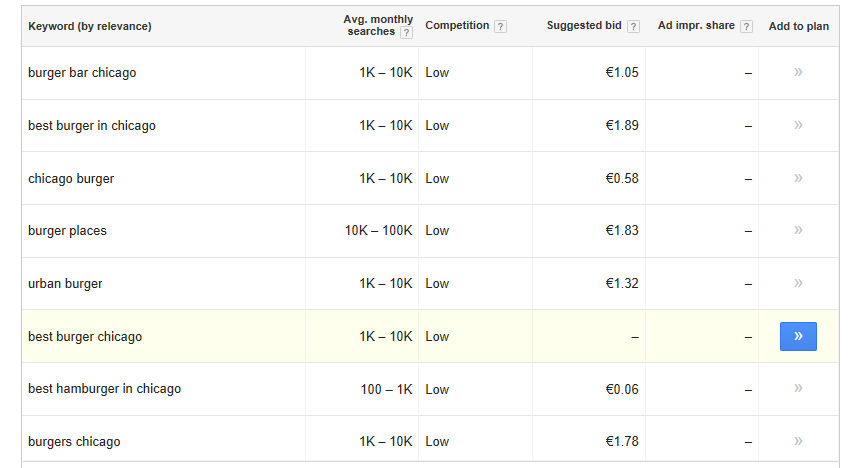
Examining Relevant Keywords:
• "burger bar Chicago" fits our business well, draws 1K-10K monthly searches, and faces low competition. This could be a good keyword to consider.
• "best burger in Chicago" is also closely related to what we offer, with a monthly search volume of 1K-10K and low competition, making it another strong choice.
How to use keywords?
• "Chicago burger" is also a good fit, with 1K-10K monthly searches and low competition. This should be on our keyword list.
• "Burger places" has high search volume (10K-100K) and low competition. However, it's too broad and doesn't focus on Chicago, so we may want to skip this one.
• "Urban burger" doesn't relate to our business, so we won't include it.
• "Best burger Chicago" fits, has 1K-10K monthly searches and low competition. However, "best burger in Chicago" is a better choice for us.
• "Best hamburger in Chicago" has around 1K monthly searches and low competition. But since we're about burgers, not hamburgers, this one won't make the cut.
Take notes with pen & paper or start a new Google Sheet
Now that we've identified keywords meaning, it's time to jot them down. You can use good old-fashioned pen and paper (can you?) or go digital with a Google Sheet. Make sure to note the monthly search volume and competition level for each. Pen and paper work well for brainstorming sessions with your team. Google Sheets are convenient for ongoing use, especially when expanding your list to include keywords for specific website pages like 'Menu' or 'Location.'
Longtail keywords vs. shorttail keywords
Specific keywords make it easier to rank higher in search results and draw in the right audience. These are known as long-tail keywords. More general keywords, or keyphrases, are called short-tail keywords. For an SEO keyword example, "burger bar" is much more general compared to "burger bar in Chicago," which narrows down the search considerably.
Short-tail keywords tend to be more competitive because many businesses aim to rank for them. In contrast, long-tail keywords help you reach people who are more likely to be interested in what you offer. For instance, you might have found this blog by searching for "what are keywords" instead of just "keyword."
Using Keywords on Your Website
After you've picked your keywords, the next step is incorporating them into your website. There are multiple spots on a single page where these terms should appear.
Page Title: Your page title, also seen in the browser tab and search engine results, should include your main keyword. It's coded like this: <title>Your main keyword plus additional text</title>. The title should not just be the keyword; add some extra text to make it readable and engaging.
URL: Your web page's address is another good spot for keywords. For example, a URL like mysite.com/blog/top-places-to-visit-this-summer is better than a random string like mysite.com/blog/?p=364492. The former is easier to understand for both search engines and people.
H1 Tag: This is the main headline of your page, and it should include your key term. Make sure it stands out by being larger than the surrounding text and compelling to the reader.
Page Content: The main body of your website is prime real estate for keywords. This is where you share what sets your business apart. But a word of caution: don't overuse keywords, as this can hurt your search rankings.
Image Tag: This tag is not visible on the webpage but exists in the HTML code. It's tied to the images on your page, helping search engines understand what the images represent. For example, <img class='article-img' loading='lazy' class='article-img' loading='lazy' src="file-name-including-keyword.jpg" title="Title with keyword" alt="Description with keyword">.
Meta Description: This HTML tag offers a quick summary of your page's content, limited to 160 characters. This snippet appears in search engine results and should be unique for each page, containing relevant keywords.
Wrap-Up
Now that we know what keywords are and how to use them, here's a quick recap of important takeaways:
• Start by identifying your keywords before crafting content.
• Use keyword research tools to find the most effective terms.
• Opt for long-tail, low-competition keywords to make your site easier to find.
• Steer clear of general, high-competition keywords.
• Insert your keywords in key areas: the Title Tag, URL, H1 Tag, Meta Description, Page Content, and Image Tags.
If you're using Ucraft, you'll have the tools you need to make your site more search-engine friendly. But first, get comfortable with SEO basics, starting with keywords.
Best of luck!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are Keywords Important?
Keywords are pivotal for SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and PPC (Pay-Per-Click) marketing as they help rank higher on search engines, thereby driving quality and targeted traffic to your website.
How to Find SEO Keywords Example?
Finding the right keywords involves considering factors like search volume, competition, and relevance to your content. Tools like SEMrush can help in researching and identifying keywords that are pertinent and less competitive.
Understanding Keywords Meaning: How to Use Keywords?
Use keywords, or SEO phrases, in a balanced and natural manner within your content to avoid appearing spammy to readers and search engines. It's essential to use them in moderation to maintain a pleasant read and still rank well on search engines.
What's the Difference Between Keyphrases and Keywords?
'Keyphrases' often refer to phrases consisting of multiple words, whereas 'keywords' may consist of a single word or multiple words. Both are crucial for SEO as they help define the content and improve its visibility on search engines.
Related posts
446,005 entrepreneurs like you already have a head start
Become one of them by getting world-class expertise delivered into your inbox, for free.